I have written here about Calgary based Eavor and its effort to have scalable geothermal energy available almost anywhere. The company has begun delivering power to the German grid from its first commercial facility.
Quaise Energy is also working on delivering clean geothermal energy, using a unique deep-drilling system. The company makes these points:
- Our approach uses the established workforce, assets, supply chains, and regulatory frameworks of the fossil fuel industry.
- We can build a truly equitable, clean energy source on a global scale.
- Deep geothermal energy is at the core of an energy-independent world. It is the only renewable solution with the potential to get us to net zero by 2050. It is renewable, inexhaustible, and available everywhere.
- First, we use conventional rotary drilling to get to basement rock. Then, we switch to high-power millimeter waves to reach unprecedented depths.
- Millimeter wave drilling will unlock the most abundant and powerful clean energy source on Earth by allowing us to drill as far down as 20 km to reach temperatures up to 500° C.
- Deeper geothermal is more universal. At these depths, we can reach superhot geothermal anywhere on Earth, making it a truly global energy source. It provides a path to energy independence for every nation.
- Geothermal does not require any fuels and does not produce any waste. It’s truly renewable, abundant, and equitable for all, even in the most challenging energy environments.
- Deep geothermal uses less than 1% of the land and materials of other renewables, making it the only option for a sustainable clean energy transition.
Quaise is a spinout of MIT Energy Initiative, a major research hub at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. MITEI reported:
Quaise hosted the first of several live public demonstrations of their drilling technology that proved their technology can drill into the granite outcrop in a quarry with pure energy instead of physical drilling bits.
Quaise’s drilling system centers around a device called a gyrotron that produces millimeter waves and has been used in research and manufacturing for decades.
The September demonstration showed that they can drill through some of the hardest rock in the world at a rate of up to five meters per hour.
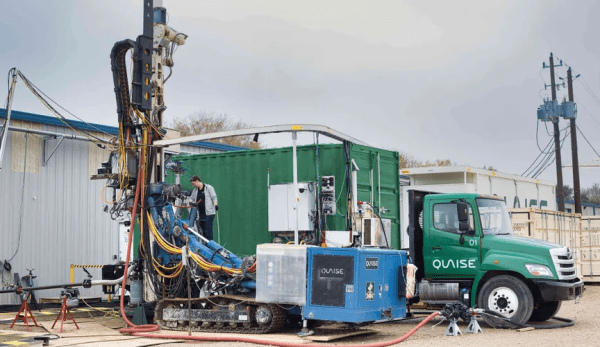
The nonprofit Canary Media discussed Quaise Energy in The smell of toasted rock could spell victory for geothermal energy. It makes these points along with others:
The more subterranean heat a geothermal plant can access, the more energy it can generate, and the Earth gets hotter closer to the core. But the intense conditions below a few miles deep rapidly wreck conventional drill bits.
[Quaise] adapted the gyrotron, a tool honed by the nuclear fusion industry that emits millimeter waves, which fall on the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and infrared waves. Fusion researchers use them to heat plasma to unfathomably high temperatures.
Quaise has plenty more work to do before it can deliver its transformative promise — and that starts with getting out of the lab and into the field.
Quaise leaders did not disclose a timeline for the company’s first commercial deep drilling. At that point, Quaise will need to build an actual power plant and navigate the myriad permitting and transmission-connection hurdles that face renewables developers broadly. The company is running this development process in-house and already has multiple geothermal leases secured, a spokesperson noted.
“Advanced geothermal technologies could unlock a terawatt-scale resource that can deliver clean energy on demand,” said Jesse Jenkins, an authority on net-zero modeling and assistant professor at Princeton University. “That would be an enormously valuable tool to have in our toolbox.”
Permitting and transmission-connection hurdles face renewable developers broadly. Raising money to gain expertise and moving systems to a commercial stage are also challenges. With geothermal energy, the potential rewards are huge, in both financial and environmental terms. British Columbia should choose to be a leader in this sector.
Categories: Geothermal



Just asking.
Does the UK have enough windfarms yet?
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cn9zyx150xdo
“The UK has awarded contracts to build a record amount of offshore wind as part of its efforts to grow the country’s clean electricity.”
“The projects span England, Scotland and Wales, including part of what could become the world’s largest offshore wind farm, off the coast of Scotland in the North Sea.”
“But some analysts warn that despite the record haul of offshore wind, the government will still struggle to meet its 2030 “clean power” target.”
“The government argues that wind projects are cheaper than new gas power stations and will “bring down bills for good”, but the Conservatives have accused its climate targets of raising energy prices.”
The government wants at least 95% of Great Britain’s electricity to come from “clean” sources by 2030, partly to help tackle climate change by reducing carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels. These clean sources include renewables – such as solar and wind – and nuclear energy.”
“Offshore wind is widely seen as the backbone of Great Britain’s future clean electricity system, with plentiful wind resources off the country’s coastlines.”
“The government wants at least 43 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind by 2030 to help meet its clean power target.”
========================================================================
How soon did India plan to be at least 50% energy reliant on renewables? 2030.
They reached their target 5 years early.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/5-years-ahead-of-target-india-gets-50-power-from-clean-sources/articleshow/122540328.cms
LikeLike
Osmatic Power?
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
Ocean solar?
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
Why Australia opted for a multi-purpose wave energy solution.
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
Energy megaprojects
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
The US abandons its own success
Belgium creates a huge wind energy consortium.
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
Flywheel energy storage?
https://www.msn.com/en-ca/news/world/this-invention-may-change-the-world-of-renewable-energy/vi-AA1R2wm8?ocid=BingHp01&cvid=6957ce9d73ef405c981ba17669f2cae5&ei=32
LikeLike
After such a terrible betrayal/insult President Trump will not be happy.
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cp372d37gxgo
32acf230-f881-11f0-953b-2d0041115217.jpg
UK to join major wind farm project with nine European countries
The UK is set to back a vast new fleet of offshore wind projects in the North Sea alongside nine other European countries including Norway, Germany and the Netherlands.
The government says the deal will strengthen energy security by offering an escape from what it calls the “fossil fuel rollercoaster”.
For the first time, some of the new wind farms will be linked to multiple countries through undersea cables known as interconnectors, which supporters say should lower prices across the region.
But it could prove controversial as wind farm operators would be able to shop around between countries to sell power to the highest bidder – potentially driving up electricity prices when supply is tight.
The UK National Grid published a paper earlier this month suggesting such an arrangement could cut so-called constraint payments, made when wind farms are asked not to generate power because the electricity network is too congested.
A separate report said UK consumers had enjoyed savings of £1.6bn from the nine existing undersea cables linking the UK with Europe since 2023.
National Grid said the cables help smooth spikes in prices because, thanks to time zone differences, surplus energy generated off-peak elsewhere can be sold cheaply to the UK.
The agreement underlines Europe’s continued commitment to wind power, despite renewed criticism from US President Donald Trump, who again attacked what he called “windmills” during a speech at the World Economic Forum in Davos.
The North Sea countries pledged to develop 300 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind capacity three years ago. This new deal means 100GW of the total will be built jointly. It is expected to say 20GW of that should be under way by 2030.
China currently leads the world in offshore wind, with 43GW of the world’s 83GW of installed capacity, according to a report last year from industry body RenewableUK.
The UK ranks second, with almost 16GW already in operation. The UK government has awarded contracts for a further 20GW, including 8.4GW agreed in a record-breaking bidding round earlier this month.
https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/wind-power-by-country
Country Wind Power Capacity Wind Power Generation
MHW TWH
CHINA 441895 885.87
US 148,020 421.14
GERMANY 69,459 137.32
INDIA 44,736 82.11
SPAIN 31,028 64.13
UK 30,215 82.31
BRAZIL 29,135 95.51
FRANCE 22,196 48.61
CANADA 16,989 38.94
LikeLike
For only 10 of 12 months BC Hydro bought energy from outside the province.
Proof positive that there’s no need to ramp up more renewable energy options like geothermal, off shore wind, etc. Just stay the course and enrich our neighbours at public expense.
https://resourceworks.com/electrification_nerc_nr/
VANCOUVER, BC – The Chair of the Energy Futures Initiative is calling for a swift response based on new information showing British Columbia emerging as an ‘at-risk area’ for energy as soon as 2026, after a year in which BC Hydro imported record amounts of electricity to help keep the lights on.
Barry Penner, who was appointed Chair for the Energy Futures Initiative last month, is pointing to the latest annual forecast published by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) stating that for British Columbia “energy risks increase in 2026 as forecasted demand increases and natural-gas-fired generation retires.” NERC did not identify such a risk for British Columbia in their report last year.
“This report is highly concerning,” said Penner. “If our energy system ceases to be reliable, we could find ourselves facing an energy crisis — one that would have a significant impact on BC residents and businesses alike.”
The independent report comes amidst a recent decision from the BC Utilities Commission (BCUC) to reject a $327 million proposal that would have increased natural gas capacity in the Okanagan. BCUC pointed in part to the government’s CleanBC policy for their decision, which calls for electricity to replace natural gas for heating.
https://thedeepdive.ca/bc-hydro-imports-record-quarter-of-provinces-power-amid-prolonged-drought/
BC Hydro brought in 13,600 gigawatt hours of electricity during fiscal year 2024—approximately one-quarter of the province’s total electricity consumption—costing nearly $1.4 billion, according to regulatory filings with the BC Utilities Commission.
The bulk of these imports came from the United States and Alberta, where fossil fuels generate a significant portion of electricity. The reliance on external power sources contrasts sharply with British Columbia’s identity as a clean energy leader, where renewable hydroelectric sources account for over 98% of domestic electricity generation.
The Energy Futures Institute, an industry group, has voiced concerns about energy security. The organization reported that most imported electricity came from US sources that derive 60% of their electricity from fossil fuels, and from Alberta’s predominantly natural gas-based grid. Barry Penner, the institute’s chairman and former environment minister, said the import level is “the first time it’s reached almost 25 per cent of our total needs.”
However, Dix emphasized that British Columbia has maintained profitability in power trading. “The power we export is worth way more than the power we import, such that the last five years, even though we’ve been importing more, we make $550 million for the ratepayers on the exchange,” he said.
The utility uses hydroelectric reservoirs to store energy in water form, allowing it to import electricity when prices drop and export when demand and prices peak. Over the past 16 years, the province imported electricity on a net basis in eight years and exported in eight years.
The $16 billion Site C Dam, which completed construction in August, now produces approximately 5,100 gigawatt hours of annual generation capacity. BC Hydro has also launched its first competitive call for power in over 15 years, seeking to acquire approximately 3,000 gigawatt hours per year of additional clean electricity.
Forecasters expect drought conditions to persist, potentially forcing the province to import significant power for a third consecutive year.
LikeLike